39 dosage calculations with labels
4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs Mar 18, 2022 · Nursing Interventions Rationale; Encourage patient to perform prescribes exercises. To prevent stump trauma. Provide stump care on a routine basis: inspect the area, cleanse and dry thoroughly, and rewrap stump with an elastic bandage or air splint, or apply a stump shrinker (heavy stockinette sock), for “delayed” prosthesis.: Provides an opportunity to … Oral Drug Dosage Calculator - Liquid Solution Syrup ×5 milliliter X (amount) =10 milliliter Description: This calculator determines the volume of liquid, solution or syrup to be administered to the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine. The concentration is the mass of medicine contained in a volume of liquid. The mass is the have dose.
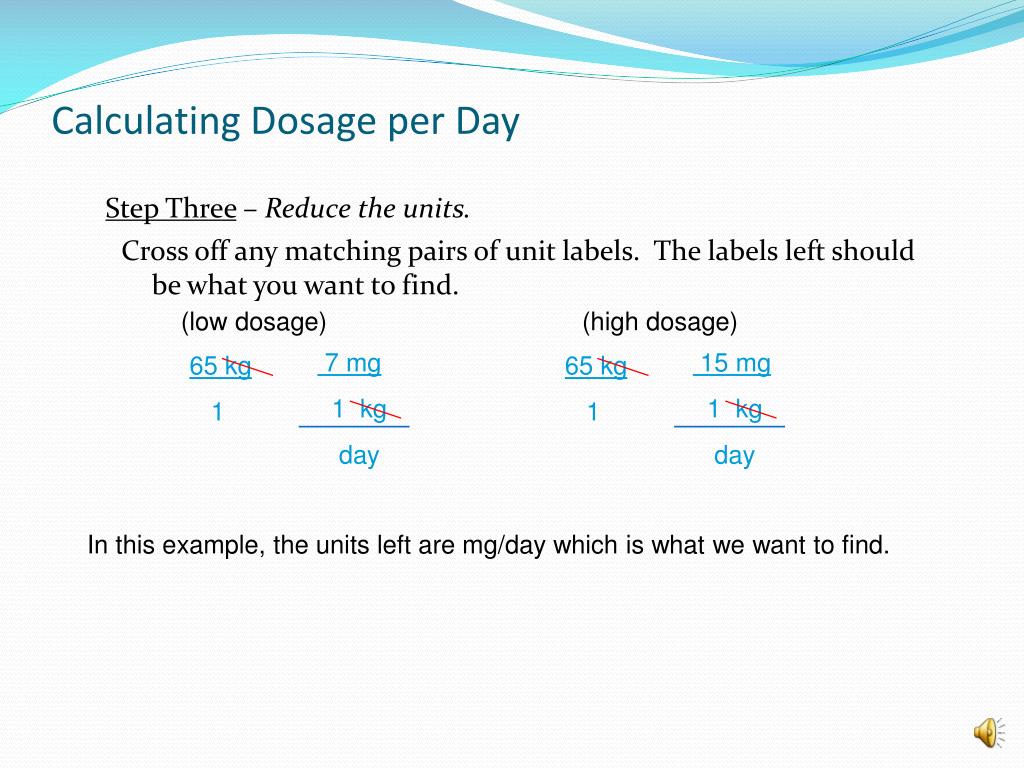
Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method A formula is used to calculate the dose of a drug, often utilized when converting different units of measurements such as pounds to kilograms or kilograms to grams. The dimensional analysis approach or the factor-label method can be used to provide an additional safety check with the other methods of calculation.

Dosage calculations with labels
getlibraryhelp.highlands.edu › cClinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and ... Feb 11, 2022 · 400 mg = 1 ml (from the reconstitution directions on the label) You do not use the 1.8 ml of diluent added in your calculations, but you need this information to find the 400 mg per ml after reconstitution from the drug label. Equation for the dose in ml: Please notice: One day = 24 hours. Every 8 hours = 3 doses per day Dose Calculation Desired Over Have Formula Method - StatPearls - NCBI ... 1 pint = 2 cups 12 inches = 1 foot 1 L = 1.057 qt 1 lb = 16 oz 1 tbsp = 3 tsp 60 minute = 1 hour 1 cc = 1 mL 2 pints = 1 qt 8 oz = 240 mL = 1 glass 1 tsp = 60 gtt 1 pt = 500 mL = 16 oz 1 oz = 30 mL 4 oz = 120 mL (Casey, 2018) Technique There are 3 primary methods for the calculation of medication dosages, as referenced above. › nclex › dosage-calculationsDosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN || RegisteredNursing.org Feb 04, 2022 · Calculating Oral Medication Dosages Using Ratio and Proportion. Here is an example of how to calculate oral medication dosage using ratio and proportion: Doctor's order: 125 mg of medication once a day. Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg. How many tablets should be administered daily?
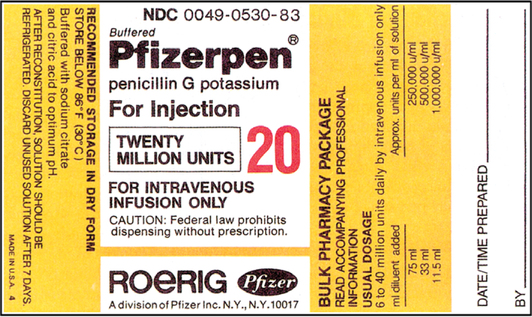
Dosage calculations with labels. PDF Dosage Calculations Module Mastery Problem Answers The doctor orders a drug dosed at 0.4g po tid. The stock supply for the drug is 150mg/mL. How many milliliters will you give for the correct dose? a. 2.7 mL b. 1.7 mL c. 2.4 mL d. 6.7 mL Answer = mL g mg mg g mL 2.7 1 1000 150 1 1 0.4 ⋅× × = MASTERY PROBLEM 5 The doctor orders a drug 0.6g po tid. The stock supply of the drug is 200mg tablets. PDF Preparing for the Drug Dosage Calculation Competency Exam BSN ... 16. The provider orders 125mg of amoxicillin Q. 8 hrs. for a patient weighing 58 lbs. Calculate the daily dosage range recommended on the label and compare the daily dose ordered by the doctor. Does the provider order fall within the usual dosage range? 17. Aggrastat is ordered to infuse at 0.1 mcg/kg/min for a patient weighing 136 lbs. A ... › drug-dosage-calculationsDrug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide + Quiz | KnowledgeDose Sep 20, 2019 · In part 2, you will find worked examples (with steps) on how to calculate the required number of tablets or volume of liquid medicine. Finally, in part 3, you can test what you have learnt by attempting the drug calculations quiz. Let us get started. Drug Dosage Calculation Formulas. To calculate the number of tablets, use the following formula: Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the milliliters of Augmentin ...
Drug Calculations: How to Calculate Drops Per Minute Dec 06, 2021 · Cancel the labels. What you are left with are drops (gtts) multiplied by the infusion rate divided by 60. You can rearrange the equation and divide the drops (gtts) by 60 and multiply by infusion rate. ... As easy as 1, 2, 3! Dosage calculations. Nursing Made Incredibly Easy!, 11(1), 25 – 29. Wilson, K.M. (2013). The nurse’s quick guide to ... Calculating from the labels | Learning Lab This short video is the second of three videos in the Nursing calculations - Finding the volume required section. It explains how to calculate medication dosage from labels using the method of mental calculation and proportinality to get the right dosage for drugs in solution. Nursing calculations: Calculating from the labels Watch on Transcript › en-us › documentDosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels - Dosage Calculation ... Dosage Calculation: Reading Drug Labels Chapter 11. Tarleton State University NURS 3310 Dr. Mary B. Winton. Reading Drug Labels. a. Brand/trade name b. Generic name c. Formulation d. Dosage strength e. Route f. Need prescription or Over -the-counter. Reading Drug Labels and Reconstitution. a. Generic name b. Brand/trade name c. Formulation d ... PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration
Nursing Dosage Med Math Calculations Math You need to infuse 500 ml Vancomycin over 3 hours. The drop rate of your infusion rate is 20 gtt/min. Let's change our hours to minutes… 3 x 60 = 180 minutes. (500 ml ÷ 180 min) x 20 = 55.55554. Let's round-up for our final answer to be 56 gtt/min. Med Math Step 6: Calculate the dosage - Dimensional Analysis Nursing. Dosage calculations review with labels - YouTube This project was created with Explain Everything™ Interactive Whiteboard for iPad. Nursing Pharmacology: Dosage and Calculations Practice Test The medication label reads "1,200,000 units per 2 mL." The nurse has determined that the dose prescribed is safe. The nurse administers how many milliliters per dose to the child? a. 0.8 mL b. 1.2 mL c. 1.4 mL d. 1.7 mL 19. Atropine sulfate, 0.6 mg intramuscularly, is prescribed for a child preoperatively. Dosage and Calculations - Registered Nurse RN Some types of dosage calculations require you to determine the dosage of a medication or the amount to be administered based on the prescribing provider's order and the patient's weight. These types of drug problems require converting pounds to kilograms and that you apply that […] Tablets and Capsules Dosage Calculations (Desired over Have Method)

17 Best images about Dosage Calculations on Pinterest | Equation, Nursing students and Dosage ...
Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA
PDF Study Guide with Sample Questions Dosage Calculation Competency • The dosage calculation competency test is given as a proctored assessment in the college's Testing Center, located in the Library in Martin Hall. ... The label on the I.V. bag reads: Heparin 10,000 units in 500 mL D 5 W. How many mL/hr will deliver the correct dose? 13._Administer Heparin 1,000 units/hr from an l.V. bag mixed 40,000 units ...
PDF Dosage Calculations Cheat Sheet - NursingSOS Dosage Calculations Cheat Sheet LEGAL DISCLAIMER: This cheat sheet is intended for educational purposes only. This is not medical advice and errors may occur. Never treat a patient or make a nursing or medical decision based solely on the information provided in this video. Never practice nursing or medicine unless you have a proper license to ...
› math104 › lecture3Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage ... Reading Medication Labels and Calculating Dosages Reading Medication Labels . Before we can even begin to calculate how much medicine to give a patient, we must be able to read a medication label correctly. There are several important pieces of information we should look for whenever we look at a medication label: Name of the medication
Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? How to calculate drug dosage If you want to find what the appropriate dosage of a drug is for your body weight, you need to follow these steps: Determine the dosage of the medication. Let's say the appropriate dosage of the active substance is 2 mg/kg of body weight. Weigh yourself. Let's assume you weigh 80 kg.
What Does "IU" Mean in Vitamins? | livestrong Apr 16, 2019 · To make those calculations, you need to know which form of the vitamin you're dealing with and the appropriate conversion factor. If you're converting from IU to weight (mcg, mg or g), you'll divide by the conversion factor. If you're converting from weight to IU, you'll multiply by the conversion factor.
We Sent Alex Jones' Infowars Supplements To A Lab. Here's … Aug 09, 2017 · “It's like QVC for conspiracy.” One estimate by New York magazine — which uses some back-of-the-envelope calculations based on the number of reviews of supplements on Jones' Infowars Life Store — suggests that, with an average supplement price of $30, Jones could haul in $15,000,000 in sales over a two-year period. A second, less ...
Dosage Calculation Using the Formula Method - Basicmedical Key 2. Calculate medication dosages using the formula. D H × Q = x. 3. Calculate the number of tablets or capsules to administer. 4. Calculate the volume to administer for medications in solution. This chapter shows how to use a formula for dosage calculation, which requires substituting information from the problem into the formula. The nurse ...
PDF Introductory Level Drug Dosage Practice Problems 27. The doctor prescribes a daily dosage of 500 mg for a patient to be divided into two doses. Find the amount of medication in mL required for an individual dose for this patient by using the label below. Give: _____ mL Figure 2: Mycobutin (rifabutin capsules, USP) [Jpeg]. (2013). Dosage Calculations for Nurses: Know Your Labels.
Catalyst support effects on hydrogen spillover | Nature Jan 05, 2017 · a, XAS spectra at the Fe L 3 edge measured in X-PEEM during hydrogen dosage at 1 × 10 −5 mbar, demonstrating the degree of reduction of the iron oxide particles on the aluminium oxide support ...
Nursing Math - Parenteral Injectable Drug Dosage Calculator Parenteral Drug Dosage Calculator For Syringe Liquid Solutions Medicine Injectable Dosage Equations Formulas. Description: This calculator determines the liquid or solution volume to be injected by syringe into the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine. The concentration is the mass of medicine ...
Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Dimensional analysis (DA) or factor-label method uses a series of conversion factors of equivalency from one system of measurement to another but doesn't require memorizing specific formulas. This method reduces errors and can be used for all dosage calculations. To set up the equation, start with the label or unit of measure needed in the answer.
Dosage Calculation Resources - Calhoun Community College ONLY TWO ATTEMPTS allowed to obtain 90% for eligibility for enrollment. This is a 40 item exam. 36/40 required for a 90% score. 75 minutes will be allowed for test completion. Calculation problems will be fill-in-the-blank, NOT multiple choice. If you need testing accommodations contact Student Disability Services at 256-306-2630.










Post a Comment for "39 dosage calculations with labels"